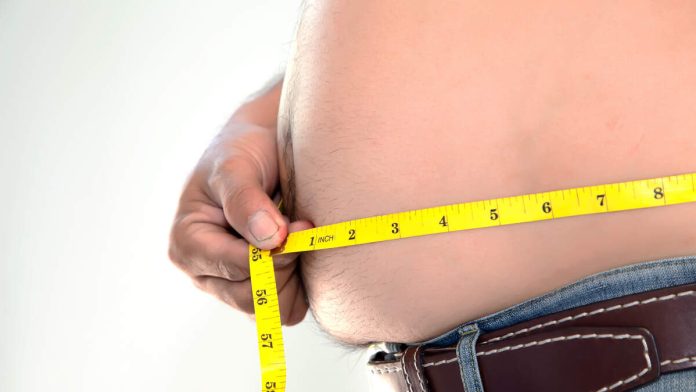
New data released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Health Statistics shows that while the overall rate of obesity among adults in the United States has declined slightly, the prevalence of severe obesity has continued to rise over the last two years.
According to the report, 40.3% of Americans aged 20 and older are considered to be obese. That’s down 1.6% from 2017 and 2020 but is still 2.6% higher than 2013 to 2014, when the rate was at 37.7%. The CDC considers somebody obese if they have a body mass index of 30 or higher.
While the obesity rate has ticked down slightly, the rate of severe obesity among adults was at 9.7%, an increase of 0.5% from 2017-2020 and a 1.5% increase between 2013 and 2014. A person is considered severely obese if their BMI is 40 or above.
Based on the statistics, over 100 million adults are obese, while 20 million are considered to be severely obese.
“While this does not represent an increase, it is important to recognize that these rates are still alarmingly high — higher than they were a decade ago — underscoring the urgent need for targeted public health strategies,” said Dr. John Brownstein, an epidemiologist and chief innovation officer at Boston Children’s Hospital, according to ABC News.
Recent Comments